- a sheath of thin, flexible material (e.g., latex) worn over the penis
- highly-effective
- also protects against sexually-transmitted disease (STD) agents such as
- rubber dome placed at the upper end of the vagina
- may be used along with spermicidal chemicals
- impermeable cap fitted over the cervix
- may be left in place until menstruation
- chemicals, such as nonoxynol 9, that inactivate sperm. Inserted into the vagina - often incorporated in sponge - prior to intercourse.
- Many formulations combining varying amounts of a synthetic
- taken for 3 weeks; then stopped to allow menstruation
- most widely-used method
- associated with a small increased risk of cardiovascular disease
- the Ortho Evra® patch releases hormones through the skin
- lasts one week
- small plastic ring inserted into the vagina
- NuvaRing® releases both an estrogen and a progestin and lasts for 3 weeks
- a progestin-only ring that blocks the menstrual cycle for 3 months
- injections containing:
- both an estrogen and a progestin (Lunelle®); given once a month
- progestin only (lasts for 12 weeks)
- capsules of a synthetic progestin are inserted under the skin (requiring a local anesthetic)
- prevents pregnancy for up to 5 years
- if pregnancy is desired sooner, is easily removed (again requiring a small incision and a local anesthetic) and normal fertility quickly returns.
The most popular formulation in the U.S., called Plan B, contains a high dose of a progestin). If taken within 72 hours after unprotected intercourse, the drug interferes with ovulation and, if ovulation has occurred, with fertilization. Even if fertilization should occur, Plan B may also block implantation.
If so many days have elapsed that implantation has occurred, RU-486 may be used.
RU-486 is a synthetic steroid related to progesterone. Unlike the progestins discussed above, that mimic the action of progesterone, RU-486 blocks the action of progesterone. (Synthetic molecules that mimic the action of a natural molecule are called agonists; those that oppose it are antagonists.)
RU-486 (also known as mifepristone) is a progesterone antagonist. It binds to the progesterone receptor, and in so doing prevents progesterone itself from occupying its receptor. Thus the gene transcription normally turned on by progesterone is blocked, and the proteins necessary to begin and maintain pregnancy are not synthesized. [More]
Because RU-486 is used after implantation, it is causing an early abortion and thus has been subjected to controversy.
- For centuries camel drivers in northern Africa inserted a stone in the uterus of their female camels before starting on a long trek. This prevented the animal from becoming pregnant on the journey.
- The intrauterine device (IUD) used by some 2% of U.S. women accomplishes the same purpose. It must be inserted by a physician.
- A variety of materials (usually containing some copper) and shapes work, leading one to suspect that it is simply the presence of a foreign body within the uterus that does the job.
- However, some IUDs have caused such bad side effects (e.g., infections of the uterus and fallopian tubes) that only two types remain on the U.S. market. One that does is
- Mirena® which also releases a progestin and can be left in place for up to 5 years.
- An egg can be fertilized only during the day or so after ovulation.
- Sperm can live in the female reproductive tract for up to 6 days.
- So copulation that takes place more than 5 days before or 2 days after ovulation is unlikely to lead to pregnancy.
- Abstinence during this period is called natural family planning or the rhythm method.
- Its success (which is low) depends upon being able to determine accurately just when ovulation occurs.
- Highly-motivated women can do this by
- monitoring their body temperature (which rises slightly at ovulation)
- the amount and consistency of the mucus secreted by their uterus, and - more recently
- measuring the concentration of estrogen and/or progesterone in the urine (which mirrors the level in the blood).
- It is favored by those who do not currently want a baby, but do not wish to use contraceptive devices (about 4% of U.S. couples).
- the deliberate removal of the embryo or fetus before it is ready for birth
- Done
- mechanically
- using a suction device (during the first 3 months of pregnancy)
- using surgery (later in pregnancy)
or
- chemically (using RU-486 and prostaglandins - Link) during the first 7 weeks of pregnancy
All methods of birth control have been the subject of controversy (except for natural family planning).
- In general, the controversy over a given method is proportional to the lateness of the stage of the reproductive process.
- So not surprisingly, abortion is a particularly controversial procedure, especially when it is induced in the later stages of pregnancy.
- Nevertheless, worldwide it is the most common method of birth control.
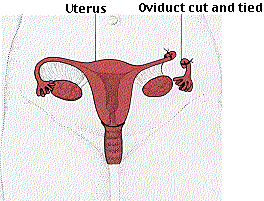 Roughly one-third of U.S. couples still in their reproductive years have chosen for one or the other to be sterilized.
Roughly one-third of U.S. couples still in their reproductive years have chosen for one or the other to be sterilized.
- The fallopian tubes (both of them!) are cut and tied so that no egg can be fertilized.
- Requires incision(s) and so must be done under anesthesia.
- Each vas deferens is cut near the top of the scrotum.
- can be done in the doctor's office, with a local anesthetic, in 30-40 minutes
- Testosterone secretion by the testes is not inhibited.
- does not stop the production of the various glandular secretions that make up the bulk of the semen so
- copulation and ejaculation proceed normally.
- Sometimes the operation can be reversed, but don't count on it.
- Pellets of the antimalarial drug quinicrine are placed (by a physician) in the uterus
- done twice, a month apart.
- causes scarring of the fallopian tubes
- Clinical trials are in progress in the U.S.
| Popularity and relative effectiveness of several methods of birth control. Popularity (% using the method) is based on a survey of U.S. couples whether married or not. The pregnancy rate is the number of pregnancies per 100 women in the first year of using the method. The women in this study were aged 15-44, lived in the United States, and were married. The lower values are apt to be found among well-educated women who are highly-motivated to practice birth control. |
|---|
| Method |
Popularity |
Pregnancy Rate |
| Natural family planning (rhythm) |
2.3% |
8-19 |
| Condom |
13.3% |
1-10 |
| Diaphragm |
< 3.6% |
6-14 |
| Oral contraceptives ("the pill") |
15.6% |
1-2.5 |
| Intrauterine devices (IUD) |
0.7% |
1.5-5 |
| Sterilization |
37% |
0 |
| None |
24% |
85-90* |
| *assuming normal fertility |
- Not too bright because pharmaceutical houses are reluctant to invest the huge amounts of money and time needed to develop products that
- expose them to controversy
- put them at risk of lawsuits and
- whose largest market is in countries too poor to afford them.
- Some research on possible male contraceptives is going on. However, it is not yet easy to see how spermatogenesis can be blocked without causing undesirable side-effects.
- Some research is proceeding on contraceptive vaccines; that is, using the immune system to block one or another step in the process (e.g. fertilization). Examples:
But, what risks such antibodies might present is not at all clear.
18 November 2005
 Roughly one-third of U.S. couples still in their reproductive years have chosen for one or the other to be sterilized.
Roughly one-third of U.S. couples still in their reproductive years have chosen for one or the other to be sterilized.