One of the best definitions is that of the evolutionary biologist Ernst Mayr:
A species is an actually or potentially interbreeding population that does not interbreed with other such populations when there is opportunity to do so.
Note: sometimes breeding may take place (as it can between a horse and a donkey) but if so, the offspring are not so fertile and/or well adapted as the parents (the mule produced is sterile).
The formation of two or more species often (some workers think always!) requires geographical isolation of subpopulations of the species. Only then can natural selection or perhaps genetic drift produce distinctive gene pools.
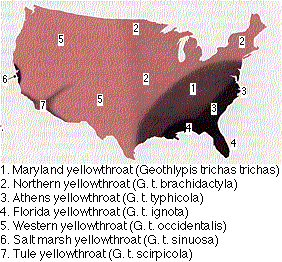
It is no accident that the various races (or "subspecies") of animals almost never occupy the same territory. Their distribution is allopatric ("other country").
The seven distinct subspecies or races of the yellowthroat Geothlypis trichas in the continental U.S. would soon merge into a single homogeneous population if they occupied the same territory and bred with one another.
As a young man of 26, Charles Darwin visited the Galapagos Islands off the coast of Ecuador.
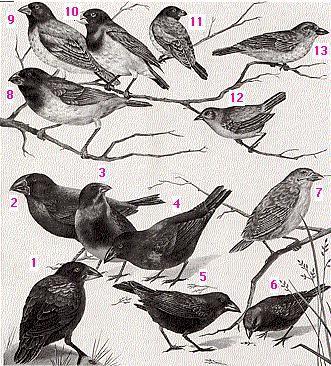
Among the animals he studied were 13 species of finches found nowhere else on earth.
- Some have stout beaks for eating seeds of one size or another (#2, #3, #6).
- Others have beaks adapted for eating insects or nectar.
- One (#7) has a beak like a woodpecker's. It uses it to drill holes in wood, but lacking the long tongue of a true woodpecker, it uses a cactus spine held in its beak to dig the insect out.
- One (#12) looks more like a warbler than a finch, but its eggs, nest, and courtship behavior is like that of the other finches.
Darwin's finches. The finches numbered 1–7 are ground finches. They seek their food on the ground or in low shrubs. Those numbered 8–13 are tree finches. They live primarily on insects.
1. Large cactus finch (Geospiza conirostris)
2. Large ground finch (Geospiza magnirostris)
3. Medium ground finch (Geospiza fortis)
4. Cactus finch (Geospiza scandens)
5. Sharp-beaked ground finch (Geospiza difficilis)
6. Small ground finch (Geospiza fuliginosa)
7. Woodpecker finch (Cactospiza pallida)
8. Vegetarian tree finch (Platyspiza crassirostris)
9. Medium tree finch (Camarhynchus pauper)
10. Large tree finch (Camarhynchus psittacula)
11. Small tree finch (Camarhynchus parvulus)
12. Warbler finch (Certhidia olivacea)
13. Mangrove finch (Cactospiza heliobates)
(From BSCS, Biological Science: Molecules to Man, Houghton Mifflin Co., 1963) |
 |
Since Darwin's time, these birds have provided a case study of how a single species reaching the Galapagos from Central or South America could — over a few million years — give rise to the 13 species that live there today.
Several factors have been identified that may contribute to speciation.
When the ancestor of Darwin's finches reached the Galapagos, it found
- no predators (There were no mammals and few reptiles on the islands.)
- few, if any, competitors. There were only a handful of other types of songbirds. In fact, if true warblers or woodpeckers had been present, their efficiency at exploiting their niches would surely have prevented the evolution of warblerlike and woodpeckerlike finches.
The proximity of the various islands has permitted enough migration of Darwin's finches between them to enable distinct island populations to arise. But the distances between the islands is great enough to limit interbreeding between populations on different islands. This has made possible the formation of distinctive subspecies (= races) on the various islands.
The importance of geographical isolation is illuminated by a single, fourteenth, species of Darwin's finches that lives on Cocos Island, some 500 miles to the northeast of the Galapagos.
The first immigrants there must also have found relaxed selection pressures with few predators or competitors.
How different the outcome, though. Where one immigrant species gave rise to at least 13 on the scattered Galapagos Islands, no such divergence has occurred on the single, isolated Cocos Island.
In isolation, changes in the gene pool can occur through some combination of
These factors may produce distinct subpopulations on the different islands. So long as they remain separate (allopatric) we consider them races or subspecies. In fact, they might not be able to interbreed with other races but so long as we don't know, we assume that they could.
How much genetic change is needed to create a new species?
Perhaps not as much as you might think. For example, changes at one or just a few gene loci might do the trick. For example, a single mutation altering flower color or petal shape could immediately prevent cross-pollination between the new and the parental types (a form of prezygotic isolating mechanism).
The question of their status — subspecies or true species — is resolved if they ever do come to occupy the same territory again (become sympatric). If successful interbreeding occurs, the differences will gradually disappear, and a single population will be formed again. Speciation will not have occurred.
If, on the other hand, two subspecies reunite but fail to resume breeding, speciation has occurred and they have become separate species.
An example: The medium tree finch Camarhynchus pauper is found only on Floreana Island.
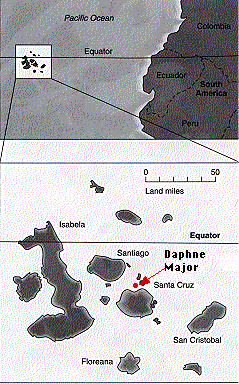 Its close relative, the large tree finch, Camarhynchus psittacula, is found on all the central islands including Floreana.
Its close relative, the large tree finch, Camarhynchus psittacula, is found on all the central islands including Floreana.
Were it not for its presence on Floreana, both forms would be considered subspecies of the same species. Because they do coexist and maintain their separate identity on Floreana, we know that speciation has occurred.
What might keep two subpopulations from interbreeding when reunited geographically?
There are several mechanisms.
These act before fertilization occurs.
- Failure to elicit mating behavior. On Floreana, Camarhynchus psittacula has a longer beak than Camarhynchus pauper, and the Grants have demonstrated that beak size is an important criterion by which Darwin's finches choose their mates.
- Two subpopulations may occupy different habitats in the same area and thus fail to meet at breeding time.
- In plants, a shift in the time of flowering can prevent pollination between the two subpopulations.
- Structural differences in the sex organs may become an isolating mechanism.
- The sperm may fail to reach or fuse with the egg.
These act even if fertilization does occur.
- Even if a zygote is formed, genetic differences may have become so great that the resulting hybrids are less viable or less fertile than the parental types. The sterile mule produced by mating a horse with a donkey is an example.
-
Sterility in the males produced by hybridization is more common than in females. In fact, it is the most common postzygotic isolating mechanism.
-
When Drosophila melanogaster attempts to mate with its relative Drosophila simulans, no viable males are even produced. Mutations in a single gene (encoding a component of the nuclear pore complex) are responsible.
Although hybridization between related species of angiosperm also causes reduced fertility, it is sometimes followed by a doubling of the chromosome number. The resulting polyploids are now fully fertile with each other although unable to breed with either parental type. A new species has been created. This appears to have been a frequent mechanism of speciation in angiosperms.
Even without forming a polyploid, interspecific hybridization can occasionally lead to a new species of angiosperm. Two species of sunflower, the "common sunflower", Helianthus annuus, and the "prairie sunflower", H. petiolaris, grow widely over the western half of the United States. They can interbreed, but only rarely are fertile offspring produced.
However, Rieseberg and colleagues have found evidence that successful hybridization between them has happened naturally in the past. They have shown that three other species of sunflower (each growing in a habitat too harsh for either parental type) are each the product of an ancient hybridization between Helianthus annuus and H. petiolaris. Although each of these species has the same diploid number of chromosomes as the parents (2n = 34), they each have a pattern of chromosome segments that have been derived, by genetic recombination, from both the parental genomes. They demonstrated this in several ways, notably by combining RFLP analysis with the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
They even went on to produce (at a low frequency) annuus x petiolaris hybrids in the greenhouse that mimicked the phenotypes and genotypes of the natural hybrids. (You can read about the results of these monumental studies in the 29 August 2003 issue of Science.)
Another example. In Pennsylvania, hybrids between
- a species of fruit fly (not Drosophila) that feeds on blueberries and
- another species (again, not Drosophila) that feeds on snowberries
feed on honeysuckle where they neither
- encounter competition from their parental species nor
- have an opportunity to breed with them (no introgression).
(You can read about the this study in the 28 July 2005 issue of Nature.)
So speciation can occur as a result of hybridization between two related species, if the hybrid
- receives a genome that enables it to breed with other such hybrids but
- not breed with either parental species;
- can escape to a habitat where it does not have to compete with either parent;
- is adapted to live under those new conditions.
The process of speciation is often hastened when two formerly isolated groups are reunited. Even if they no longer interbreed, they are probably still similar in many ways, including their requirements for the necessities of life.
Thus the reuniting of the two groups may create an intense selection pressure leading to one of two possible outcomes.
- The competition may be so intense that one species becomes eliminated entirely; that is, it is driven to extinction on that island. This may have occurred to C. pauper on some of the central islands.
- Alternatively, the increased selection pressure may lead to character displacement and so lessen the competition between them.
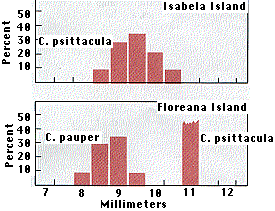
The range of beak sizes of Camarhynchus pauper on Floreana and Camarhynchus psittacula on Isabela is roughly the same. This reflects the fact that the two species feed on the same type and size of insect.
On Floreana, however, character displacement has occurred: C. psittacula has a substantially larger beak than C. pauper does, and thus differs enough in its food requirements for the two species to coexist there.
The histogram shows the data. The larger beak of C. psittacula on Floreana reduces the competition with C. pauper (which is not found on Isabela). (Redrawn with permission from David Lack, Darwin's Finches, Cambridge Univ. Press, 1947. The number of collected specimens (16) of C. psittacula on Floreana was too small to compute a reliable percentage but all fell within the range indicated.)
The process described above can occur over and over. In the case of Darwin's finches, it must have been repeated a number of times forming new species that gradually divided the available habitats between them. From the first arrival have come a variety of ground-feeding and tree-feeding finches as well as the warblerlike finch and the tool-using woodpeckerlike finch.
The formation of a number of diverse species from a single ancestral one is called an adaptive radiation.
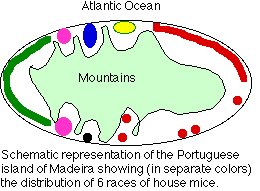 A recent (13 January 2000) report in Nature describes a study of house mouse populations on the island of Madeira off the Northwest coast of Africa. These workers (Janice Britton-Davidian et al) examined the karyotypes of 143 house mice (Mus musculus domesticus) from various locations along the coast of this mountainous island.
Their findings:
A recent (13 January 2000) report in Nature describes a study of house mouse populations on the island of Madeira off the Northwest coast of Africa. These workers (Janice Britton-Davidian et al) examined the karyotypes of 143 house mice (Mus musculus domesticus) from various locations along the coast of this mountainous island.
Their findings:
- There are 6 distinct populations (shown by different colors)
- Each of these has a distinct karyotype, with a diploid number less than the "normal" (2N=40).
- The reduction in chromosome number has occurred through Robertsonian fusions. Mouse chromosomes tend to be acrocentric; that is, the centromere connects one long and one very short arm. Acrocentric chromosomes are at risk of translocations that fuse the long arms of two different chromosomes with the loss of the short arms.
- The different populations are allopatric; isolated in different valleys leading down to the sea.
- The distinct and uniform karyotype found in each population probably arose from genetic drift rather than natural selection.
- The 6 different populations are technically described as races because there is no opportunity for them to attempt interbreeding.
- However, they surely meet the definition of true species. While hybrids would form easily (no prezygotic isolating mechanisms), these would probably be infertile as proper synapsis and segregation of such different chromosomes would be difficult when the hybrids attempted to form gametes by meiosis.
Sympatric speciation refers to the formation of two or more descendant species from a single ancestral species all occupying the same geographic location.
Some evolutionary biologists don't believe that it ever occurs. They feel that interbreeding would soon eliminate any genetic differences that might appear.
But there is some compelling (albeit indirect) evidence that sympatric speciation can occur.
The three-spined sticklebacks, freshwater fishes, that have been studied by Dolph Schluter (who received his Ph.D. for his work on Darwin's finches with Peter Grant) and his current colleagues in British Columbia, provide an intriguing example that is best explained by sympatric speciation.
They have found:
- Two different species of three-spined sticklebacks in each of five different lakes.
- a large benthic species with a large mouth that feeds on large prey in the littoral zone
- a smaller limnetic species — with a smaller mouth — that feeds on the small plankton in open water.
- DNA analysis indicates that each lake was colonized independently, presumably by a marine ancestor, after the last ice age.
- DNA analysis also shows that the two species in each lake are more closely related to each other than they are to any of the species in the other lakes.
- Nevertheless, the two species in each lake are reproductively isolated; neither mates with the other.
- However, aquarium tests showed that
- the benthic species from one lake will spawn with the benthic species from the other lakes and
- likewise the limnetic species from the different lakes will spawn with each other.
- These benthic and limnetic species even display their mating preferences when presented with sticklebacks from Japanese lakes; that is, a Canadian benthic prefers a Japanese benthic over its close limnetic cousin from its own lake.
- Their conclusion: in each lake, what began as a single population faced such competition for limited resources that
- disruptive selection — competition favoring fishes at either extreme of body size and mouth size over those nearer the mean — coupled with
- assortative mating — each size preferred mates like it
favored a divergence into two subpopulations exploiting different food in different parts of the lake.
- The fact that this pattern of speciation occurred the same way on three separate occasions suggests strongly that ecological factors in a sympatric population can cause speciation.
Sympatric speciation driven by ecological factors may also account for the extraordinary diversity of crustaceans living in the depths of Siberia's Lake Baikal.
There is another possible way for new species to arise in the absence of geographical barriers.
- If a population ranges of a vast area (e.g., the Amazon basin in south America) and
- if the individuals in that population can disperse over only a small portion of this range,
then gene flow across these great distances would be reduced.
Genetic isolation arising simply from the great distance separating subpopulations could thus lead to "parapatric" speciation. Some workers feel that the enormous species diversity of the rain forests of South America (greater than that of Africa and Asia combined!) arose from parapatric speciation.
3 August 2005


 Its close relative, the large tree finch, Camarhynchus psittacula, is found on all the central islands including Floreana.
Its close relative, the large tree finch, Camarhynchus psittacula, is found on all the central islands including Floreana.

 A recent (13 January 2000) report in Nature describes a study of house mouse populations on the island of Madeira off the Northwest coast of Africa. These workers (Janice Britton-Davidian et al) examined the karyotypes of 143 house mice (Mus musculus domesticus) from various locations along the coast of this mountainous island.
Their findings:
A recent (13 January 2000) report in Nature describes a study of house mouse populations on the island of Madeira off the Northwest coast of Africa. These workers (Janice Britton-Davidian et al) examined the karyotypes of 143 house mice (Mus musculus domesticus) from various locations along the coast of this mountainous island.
Their findings: