| Index to this page |
The human genome is presently estimated to contain 20–25 thousand genes. The number of T-cell receptors for antigen (TCRs) that we make is estimated at 2.5 x 107; the number of different kinds of antibody molecules (BCRs) is probably about the same.
| Link to discussion of the structure of BCRs and TCRs. |
How could 2.5 x 104 genes encode 2.5 x 107 different TCRs and the same number of different BCRs?
The answer: each receptor chain
The genome contains a pool of gene segments for each type of chain. Random assortment of these segments makes the largest contribution to receptor diversity.
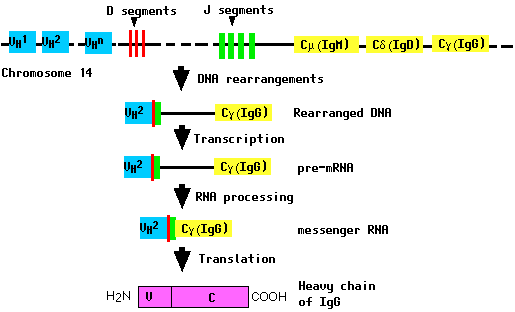
During the differentiation of the B cell (and long before any possible encounter with an antigen), the DNA in this locus is cut and recombined to make an intact gene for the heavy chain. This gene can then be transcribed into mRNA, which is, in turn, translated into the heavy (H) polypeptide chain.
| External Link |
| To see an animation of V(D)J joining, click immunobiology and navigate to "Antigen Recognition" -> "somatic recombination" (Requires Flash 5). |
| Please let me know by e-mail if you find a broken link in my pages.) |
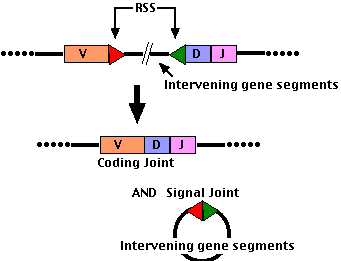
Some cases of severe combined immunodeficiency in humans (SCID) are caused by defects in V(D)J joining.
|
The random assembly of 51 VH, 27 DH, and 6 JH gene segments provides a minimum of 8.3 x 103 different possible combinations.
But the possibilities of antibody V region diversity turn out to be greater than that. The recombination process is not precise.| Antibodies (BCRs) | Gene Segments | Combinations |
|---|---|---|
| Vκ | 40 | |
| Jκ | 5 | 200 κ chains |
| Vλ | 31 | |
| Jλ | 4 | 124 λ chains |
| VH | 51 | |
| DH | 25 | |
| JH | 6 | 7,650 H chains |
| Any H chain with any L chain (324) | 2.5 x 106 | |
As the table shows, this lays the foundation for a potential B-cell repertoire of 2.5 x 106 different antibody V regions. But the true number is probably virtually limitless because of
The diversifying mechanisms described above take place before the B cell encounters antigen. After a B cell encounters antigen, it may begin mitosis, growing into a clone of cells synthesizing the same BCR (and, eventually, secreting antibodies with the same binding site). Point mutations can occur while this is going on. Some of these may generate a binding site with increased affinity for its epitope. These are favorable mutations, and the "subclone" in which they occur tends to be favored and may replace the ancestral clone. The result is affinity maturation — the production of antibodies of ever-increasing affinity for the antigen.
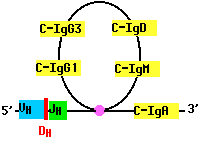
As B cells grow into a clone in response to antigen, they may rearrange their DNA once again. For example, a B cell that has assembled a complete gene for the H chain of IgM (µ), may cut the gene on the 3´ side of the assembled V-region segments and move the assembly to the 5´ side of another of its CH gene segments. Now the cell begins to make a different class of antibody, such as IgG or IgA. But the antigen specificity of the antibody remains the same because the N-terminal of the H chain remains unchanged (as does the entire L chain).
Class Switch recombination enables the body to produce antibodies with different effector functions; that is, different means of dealing with the same antigen.
The ability of a B cell to switch CH gene segments depends on its receiving help from helper T cells.
The most abundant T cells in the blood express a receptor for antigen (TCR) that is a heterodimer of two chains designated alpha (α) and beta (β). Each of these is encoded by a gene assembled from V, D, J, and C gene segments. Like BCRs, there are multiple variants of these gene segments arranged in clusters:
| T cell receptors (TCRs) | Gene segments | Combinations |
|---|---|---|
| Vα | 50 | |
| Jα | 50 | 2.5 x 103 alpha chains |
| Vβ | 20 | |
| Jβ | 13 | |
| Dβ | 2 | 520 beta chains |
| Any alpha with any beta chain | 1.3 x 106 | |
And like B cells, the greatest diversity in the receptors of αβ T cells occurs in the third complementarity determining region (CDR3) of the alpha and beta chains because of
However, T cells do not seem to use somatic mutation to increase receptor diversity. Actual measurements of the repertoire in humans reveals a figure of about 2.5 x 107.
| Link to more information on γδ T cells. |
| Welcome&Next Search |