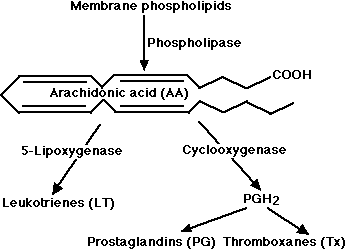
- the 5-lipoxygenase pathway, which produces a collection of leukotrienes (LT) and
- the cyclooxygenase pathway, which yields a number of prostaglandins (PG) and thromboxanes (Tx).
| Index to this page |
Immunologists, as well as the general public, use the term allergy in several different ways.
I shall define it thus:An allergy is a harmful immune response elicited by an antigen that is not itself intrinsically harmful.
Examples:These occur quickly after exposure to the allergen. They are usually mediated by antibodies of the IgE class.
Examples:| Go to discussion |
Cell damage caused by antibodies directed against cell surface antigens. Hence a form of autoimmunity.
Examples:| Go to discussion |
| Go to discussion |
| Go to discussion |
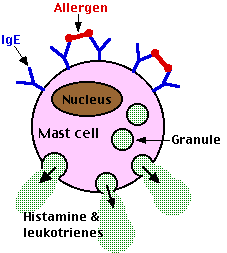
The constant region of IgE antibodies (shown in blue) has a binding site for a receptor present on the surface of basophils and their tissue-equivalent the mast cell. These cell-bound antibodies have no effect until and unless they encounter allergens (shown in red) with epitopes that can bind to their antigen-binding sites.
When this occurs, the mast cells to which they are attached explosively discharge their granules by exocytosis. The granules contain a variety of active agents including histamine and leukotrienes. Release of these substances into the surrounding tissue causes local anaphylaxis: swelling, redness, and itching. In effect, each IgE-sensitized mast cell is a tiny bomb that can be exploded by a particular antigen. The most common types of local anaphylaxis are:Leukotrienes are far more potent than histamine in mediating these reactions.
Leukotrienes and prostaglandins are derivatives of arachidonic acid (AA) an unsaturated fatty acid produced from membrane phospholipids. The principal pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism are
|
 |
Some people respond to environmental antigens (e.g., pollen grains, mold spores) with an unusually vigorous production of IgE antibodies. Why this is so is unclear; heredity certainly plays a role. In any case, the immune system of these people is tilted toward the production of T helper cells of the Th2 subtype. These release interleukin 4 (IL-4) and interleukin 13 (IL-13) on the B cells that they "help". These lymphokines promote class switching in the B cell causing it to synthesize IgE antibodies.
An inherited predisposition to making IgE antibodies is called atopy. Atopic people are apt to have higher levels of circulating IgE (up to 12 µg/ml) than is found usually (about 0.3 µg/ml). Whereas only 20–50% of the receptors on mast cells are normally occupied by IgE, all the receptors may be occupied in atopic individuals.
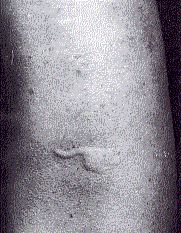
When the problem allergen is not obvious, it can often be identified by skin testing. A panel of suspected allergens is injected into separate sites in the skin and each site is observed for the development of a "wheal and flare" reaction.
TheBoth are caused by the release of leukotrienes at the site, which increase the flow of blood to the site making it swollen and red.
A positive skin test occurs within minutes or even seconds (in contrast to patch testing for DTH responses described below). In the example shown here, the antigen was 0.1 µg of protein from guinea pig hair. In some patients, a response can be elicited by as little as 0.1 ng of allergen. (Image reprinted, with permission, from B. D. Davis et al., Microbiology, 3rd ed., Harper & Row, 1980.)
Frequent causes:
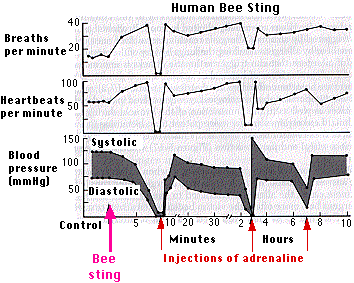 The three graphs show the physiological responses of a physician (Dr. Vick) stung by a single bee while on a picnic with coworkers (fortunately some with medical training!). Dr. Vick required cardiac massage and intravenous injections of adrenaline at the times shown. He and his colleagues worked in a laboratory studying bee venom, but prior to this episode he had no idea that he had developed such extreme susceptibility. [Courtesy of Dr. J. Vick from L. M. Lichtenstein, "Allergic Responses to Airborne Allergens and Insect Venoms", Fed. Proc. 36:1727, 1977.]
The three graphs show the physiological responses of a physician (Dr. Vick) stung by a single bee while on a picnic with coworkers (fortunately some with medical training!). Dr. Vick required cardiac massage and intravenous injections of adrenaline at the times shown. He and his colleagues worked in a laboratory studying bee venom, but prior to this episode he had no idea that he had developed such extreme susceptibility. [Courtesy of Dr. J. Vick from L. M. Lichtenstein, "Allergic Responses to Airborne Allergens and Insect Venoms", Fed. Proc. 36:1727, 1977.]
So far, the most effective preventive for IgE-mediated allergies is to inject the patient with gradually-increasing doses of the allergen itself. The goal is to shift the response of the immune system away from Th2 cells in favor of Th1 cells.
Unfortunately, this therapy takes a long time and the results are too often disappointing.
Clinical trials are now underway to test the safety and efficacy of a complex of ragweed pollen allergen with single-stranded DNA. This complex shifts the immune response from Th2 to Th1 much more rapidly than desensitization by the allergen alone.IgE molecules bind to mast cells and basophils through their constant region. If you could block this region, you could interfere with binding — hence sensitization of — these cells.
Humanized monoclonal antibodies specific for the constant region of IgE are in clinical trials. They have shown some promise against asthma and peanut allergy, but such treatment will probably have to be continued indefinitely (and will be very expensive).
Although certain other red cell antigens (in addition to Rh) sometimes cause problems for a fetus, an ABO incompatibility does not. Why is an Rh incompatibility so dangerous when ABO incompatibility is not?
It turns out that most anti-A or anti-B antibodies are of the IgM class and these do not cross the placenta. In fact, an Rh-/type O mother carrying an Rh+/type A, B, or AB fetus is resistant to sensitization to the Rh antigen. Presumably her anti-A and anti-B antibodies destroy any fetal cells that enter her blood before they can elicit anti-Rh antibodies in her.
This phenomenon has led to an extremely effective preventive measure to avoid Rh sensitization. Shortly after each birth of an Rh+ baby, the mother is given an injection of anti-Rh antibodies. The preparation is called Rh immune globulin (RhIG) or Rhogam. These passively acquired antibodies destroy any fetal cells that got into her circulation before they can elicit an active immune response in her.
Rh immune globulin came into common use in the United States in 1968, and within a decade the incidence of Rh hemolytic disease became very low.
Some people synthesize antibodies against their own red blood cells, and these may lyze the cells producing anemia. Infections, cancer, or an autoimmune disease like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are often involved. Many drugs (e.g. penicillin, quinidine) can also trigger the disorder. In these cases, stopping the drug usually brings about a quick cure.
This is an autoimmune disorder in which the patient develops antibodies against his or her own platelets (thrombocytes). The life span of the platelets may be reduced from the normal of 8 days to as little as 1 hour, and platelet counts may drop from a normal of 140,000–440,000/µl to 20,000/µl or less. This greatly interferes with normal clotting, causing
The hallmark of this autoimmune disorder is weakness of the skeletal muscles, especially those in the upper part of the body. It is caused by antibodies that attack the acetylcholine (ACh) receptors at the subsynaptic membrane of neuromuscular junctions. As the number of receptors declines, the ACh released with the arrival of a volley of nerve impulses is inadequate to generate end-plate potentials (EPPs) of the normal size. After repeated stimulation, the EPPs fail to reach the threshold needed to generate an action potential and the muscle stops responding.
| Link to discussion of the physiology of the neuromuscular junction. |
The signs and symptoms of myasthenia gravis can be quickly — but only temporarily — relieved by injecting a drug that inhibits the action of cholinesterase. This prolongs the action of ACh at the neuromuscular junction. The immunosuppressant action of corticosteroids, like prednisone, can provide long-term improvement for patients.
The exclusive role of antibodies (of the IgG class) in this disorder is demonstrated by the presence of the disease in the newborn babies of mothers with the disorder. As these antibodies, which the fetus had received from the mother's circulation, disappear (in 1–2 weeks), so do all signs of the disease.
| Links to a discussion of the |
The role of antibodies (of the IgG class) in this disorder is demonstrated by the presence of the disease in the newborn babies of mothers with the disorder. As these antibodies, which the fetus had received from the mother's circulation, disappear (in 1–2 weeks), so do all signs of the disease.
Serum sickness is caused by the many extraneous proteins present in the antiserum. Being foreign to the recipient, an active immunity develops against these proteins. The resulting antibodies bind to them forming immune complexes. These are carried by the blood and deposited in the walls of blood vessels as well as in the glomeruli of the kidneys.
Antigen-antibody complexes bind to a system of serum proteins collectively known as complement. The complex of antigen-antibody-complement attracts basophils and mast cells and causes them to release their histamine and leukotrienes producing inflammation.
Thanks to nearly universal active immunization against both tetanus and diphtheria, serum sickness is now quite rare. However, kidney damage (called glomerulonephritis) produced by deposits of immune complexes is found in other ailments.Repeated exposure to airborne organic particles, like mold spores, can elicit formation of antibodies. When these interact with inhaled antigen, inflammation of the alveoli occurs. The sufferer develops a cough, fever, and difficulty in breathing. Once removed from the source of antigen, the attack subsides within a few days.
Farmers exposed to moldy hay often develop this problem (technically known as extrinsic allergic alveolitis). Sugarcane workers, cheese makers, mushroom growers, pigeon fanciers, and a number of other occupational or hobby groups are apt to develop allergic alveolitis from exposure to the spores and dusts associated with their activities.
| Antigen presentation to CD4+ cells |
When a patient is unsure of what chemical is causing the dermatitis, the physician can try a patch test. Pieces of gauze impregnated with suspected allergens are placed on the skin. After 48 hours, they are removed and each site is examined for a positive response (a reddened, itching, swollen area).
In this disorder, Th1 cells attack antigens (as yet unidentified) in the joints producing tumor necrosis factor - alpha (TNF-α ) with resulting inflammation and damage to the joints.
A genetically engineered fusion protein consisting ofGraves' disease, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis are all more common in women than in men. The sex bias ranges from 9:1 for SLE to >2:1 for multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Why?
The answer is unclear, but hormones are probably involved.
A few clues: high levels of estrogen and progesterone| Welcome&Next Search |